Learn Chinese by yourself as a beginner can be a big challenge due to its pictographic writing system, unique pronunciation, and different grammar structure. If you’re looking for an effective method to start your journey of mastering Chinese, this article from Ni Hao Ma will guide you step by step in a simple and easy-to-apply way!
Steps to learn Chinese by yourself
China is the second-largest economy in the world and plays an important role in global trade. Therefore, mastering Chinese can open up many opportunities for work and study. However, not everyone has the means to attend Chinese language courses.

To help you approach learning Chinese in a more systematic way when self-studying, here is a Chinese learning roadmap for beginners that you can refer to!
Step 1: Learn Pinyin and Tones
Pinyin is a Latin-based transcription system that helps you learn how to pronounce and read Chinese even if you don’t know Chinese characters. Mastering Pinyin will help you read Chinese characters accurately from the beginning, especially when you want to quickly learn how to communicate.
Chinese has 4 main tones and 1 neutral tone (no tone), and each tone has its own pronunciation. Words with the same syllables but different tones will have completely different meanings. Therefore, you need to memorize the tones in order to pronounce the vocabulary correctly. For example:
- Tone 1 (高平调 – High-level tone): High and flat sound (mā – mother).
- Tone 2 (升调 – Rising tone): The sound rises (má – hemp).
- Tone 3 (降升调 – Falling-rising tone): The sound falls and then rises (mǎ – horse).
- Tone 4 (降调 – Falling tone): The sound drops quickly and strongly (mà – scold).
- Neutral tone: Light pronunciation, no emphasis (ma – question particle).
Step 2: Learn Chinese Character Structure and Writing Rules
After becoming familiar with Pinyin and basic pronunciation, you can begin to learn Chinese character structure. Chinese characters (汉字) are the traditional writing system of the Chinese people. Unlike Vietnamese or English, Chinese characters are not an alphabet. Chinese characters are a logographic writing system, and each character has its own pronunciation and meaning.
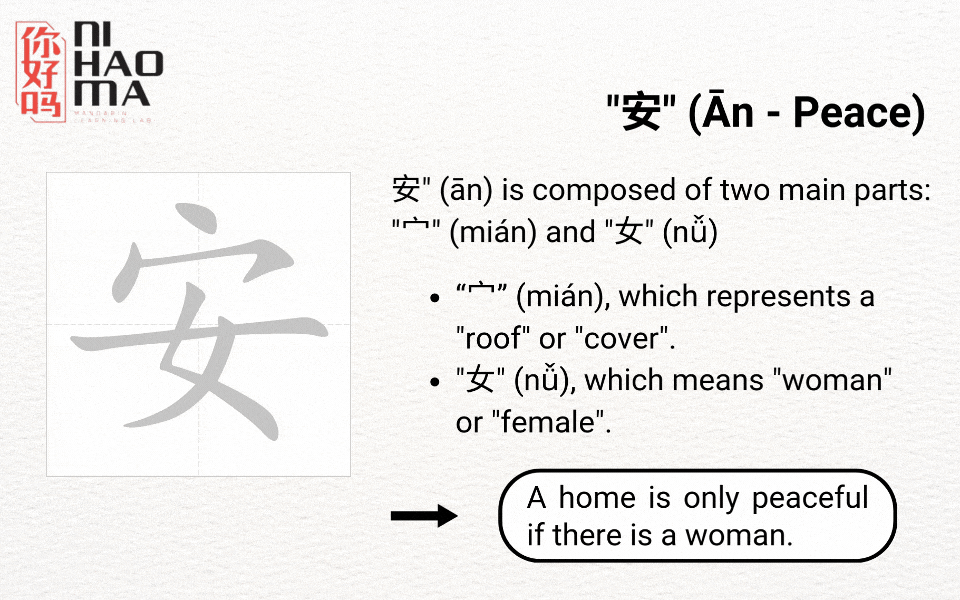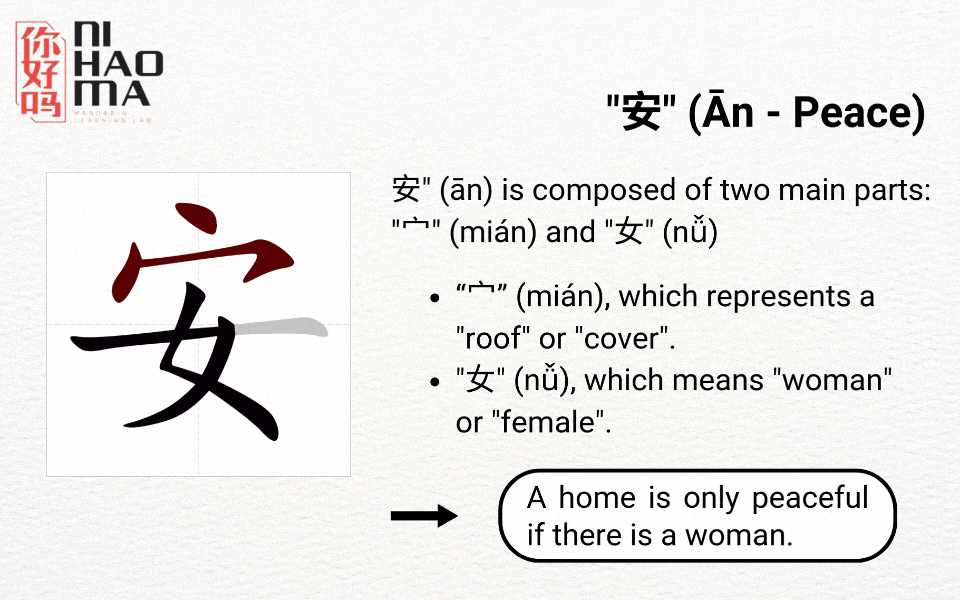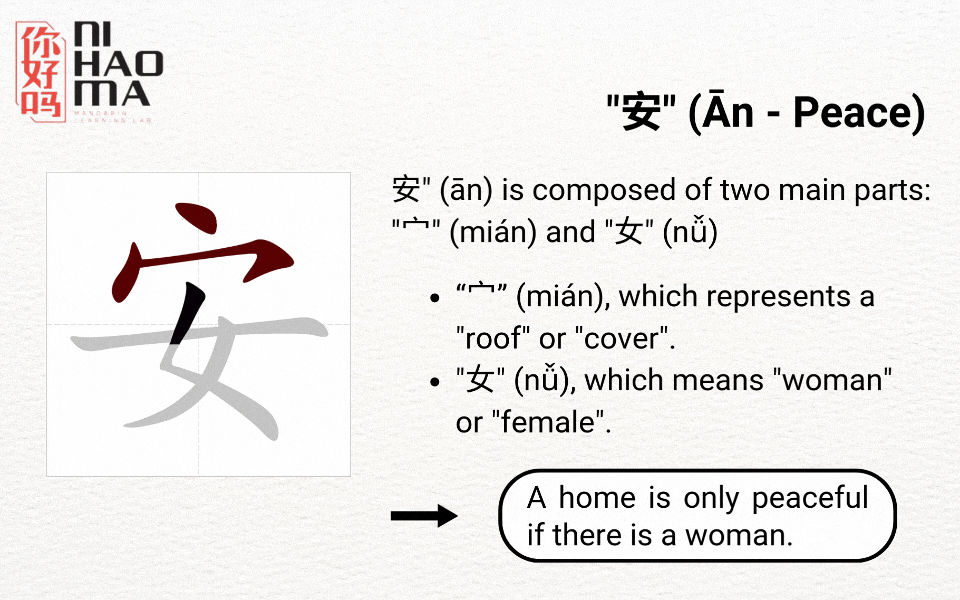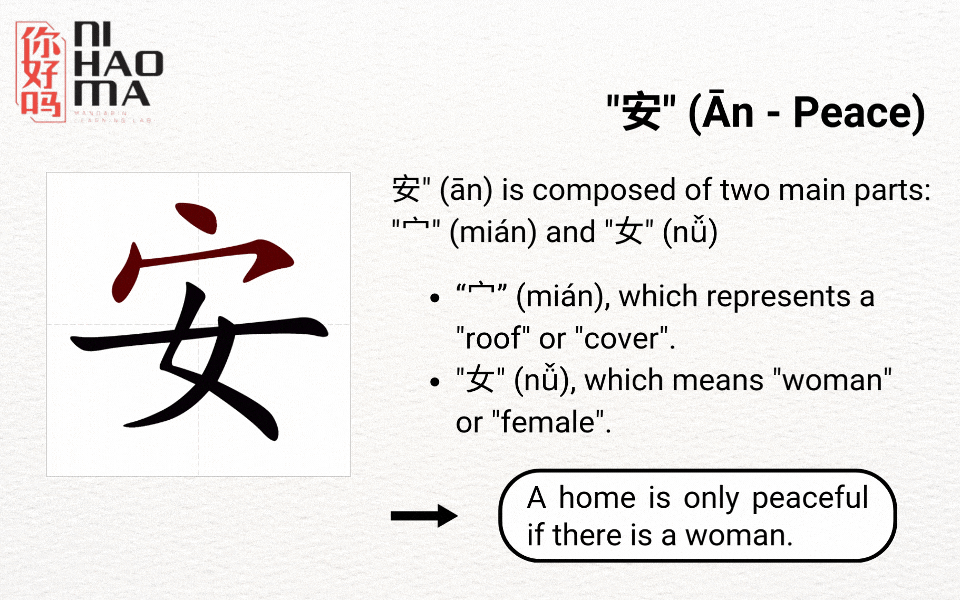
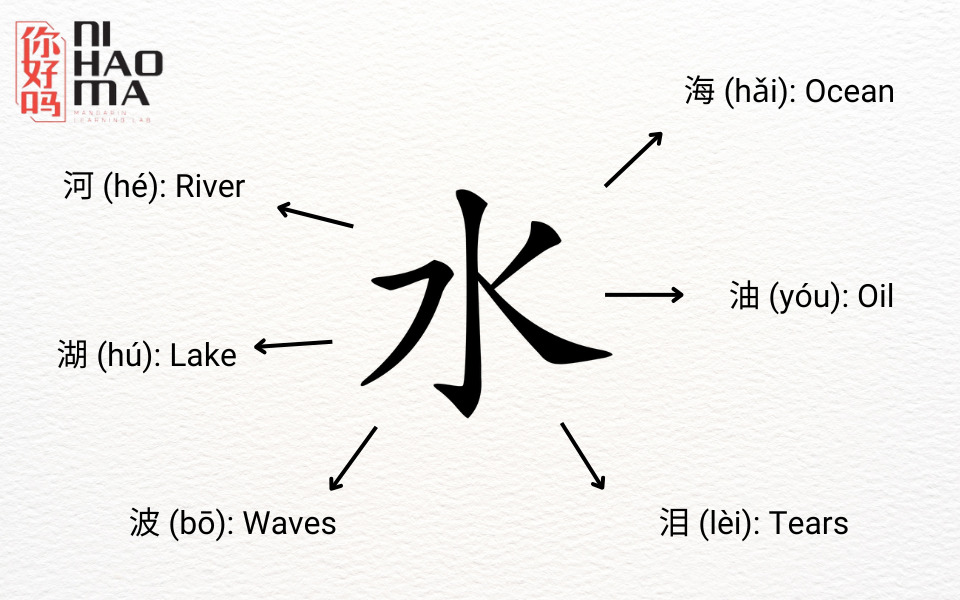
Radicals are the basic components of Chinese characters, helping you understand their meanings and remember them more easily. There are a total of 214 main radicals, ranging from simple ones (1 stroke) to more complex ones (17 strokes). Based on the radicals, you can often guess the meaning of a character. For example, the radical “水” (water) commonly appears in words related to water, such as 河 (river) and 湖 (lake).
After understanding the structure of Chinese characters, you can begin to learn the Chinese stroke order. The writing rules are basic principles that help learners write Chinese characters correctly and beautifully.
In Chinese dictionaries, there are now features that guide the stroke order of characters. If you want to practice writing, you can buy grid notebooks (or ones with sample characters) to help align the balance of the characters.
Step 3: Learn Basic Chinese Phrases
Learning basic Chinese phrases or words is an important step for communication in everyday situations. You can start with the most basic phrases such as greetings, thank you, sorry, and then continue learning more vocabulary by topic, such as shopping, eating, asking for directions, etc.

Free apps to learn Chinese like HelloChinese, Duolingo, and ChineseSkill are very popular and offer many lessons and exercises to help you master basic phrases and sentences for communication. These apps also feature pronunciation practice and speaking exercises to help you improve your pronunciation, even when studying on your own.
Step 4: Learn Chinese Grammar
By memorizing basic Chinese communication sentence patterns, you can start learning basic Chinese grammar. Nowadays, Chinese learning apps also have grammar lessons, but if you want to learn more complex grammar structures, it is advisable to buy a well-compiled Chinese textbook to build a solid foundation.
Step 5: Practice Listening and Reading Short Texts
Listening practice and reading short texts is one of the most effective methods to improve your Chinese skills. As a beginner, you should choose short and simple texts that use basic vocabulary and sentence structures. You can start with lessons from Chinese textbooks or online learning materials for beginners.

Listening practice is essential for understanding spoken Chinese during conversations with native speakers. You can choose short videos with simple content and subtitles. On your first listen, focus on grasping the main idea rather than understanding every single word. Afterward, you can listen to parts you didn’t catch clearly to learn the pronunciation and compare it with the subtitles.
Step 6: Expand Your Vocabulary
Continuously expanding your vocabulary will help you communicate more naturally and easily in real-life situations. Some effective methods to expand your vocabulary when self-learning Chinese include:
- Using flashcards: Flashcards are a learning tool that helps you remember information effectively. They have a front side (with vocabulary) and a back side (with meanings and examples). Some apps like Quizlet or Pleco can help you create digital flashcards for better vocabulary learning.
- Learning vocabulary through Chinese idioms: Chinese idioms often come from history, classical stories, or fables. Learning vocabulary through idioms not only helps you memorize words more easily but also deepens your understanding of Chinese culture.
- Learning vocabulary by topic: Choose a topic such as family, work, travel, food, etc., to easily link related words together and remember them faster.
- Reading books, watching movies, listening to music, and watching reality shows: Learning Chinese through entertainment media like movies, books, and music is not only enjoyable but also helps you get familiar with specialized vocabulary on specific topics and understand the tone and rhythm of native speakers in real conversations.
Conclusion
Ni Hao Ma has introduced how to learn Chinese by yourself for beginners. Self-learning requires a clear learning plan, discipline, and persistence. Both self-learning and attending online or offline Chinese courses have their own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, choose the learning method that suits your goals and budget!



