What is HSK? This is a question many people ask when they begin exploring the Chinese language and certification exams. Designed to assess the Chinese language proficiency of non-native speakers, the HSK certificate has become an important standard.
In this article, Ni Hao Ma will guide you through understanding what the HSK certificate is and provide insights into the HSK exam!
What is HSK?
HSK test (Hànyǔ Shuǐpíng Kǎoshì – 汉语水平考试) is a standardized Chinese proficiency test designed for non-native speakers.
The HSK is a national standardized exam organized by China to evaluate the Chinese language proficiency of learners, particularly those whose native language is not Chinese. The HSK certificate is not only a measure of language ability but also opens up numerous opportunities for studying and working in Chinese-speaking countries.

The HSK is a Chinese proficiency test focusing on three skills: Listening, Reading, and Writing. Meanwhile, the HSKK assesses Chinese speaking ability. Since 2021, many testing centers have required candidates to register for both the HSK and HSKK simultaneously to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of their skills. The HSKK level corresponds to the HSK level you register for. For example:
- HSK 3: Accompanied by the HSKK Beginner Level
- HSK 4: Accompanied by the HSKK Intermediate Level
- HSK 5, 6: Accompanied by the HSKK Advanced Level
Why choose HSK?
The HSK is an international standard for measuring your ability to use Chinese in real-life situations. HSK test is designed to assess one’s proficiency in the Chinese language, similar to how TOEFL, IELTS, and Cambridge exams evaluate English language skills.
The HSK exam assesses learners’ abilities in listening, reading, speaking, and writing, giving them a comprehensive evaluation of their Chinese language skills. Certifications from HSK are recognized by many universities, employers, and governments around the world. This means that by passing the HSK exam, you can prove your Chinese language abilities to potential employers or universities.
HSK levels
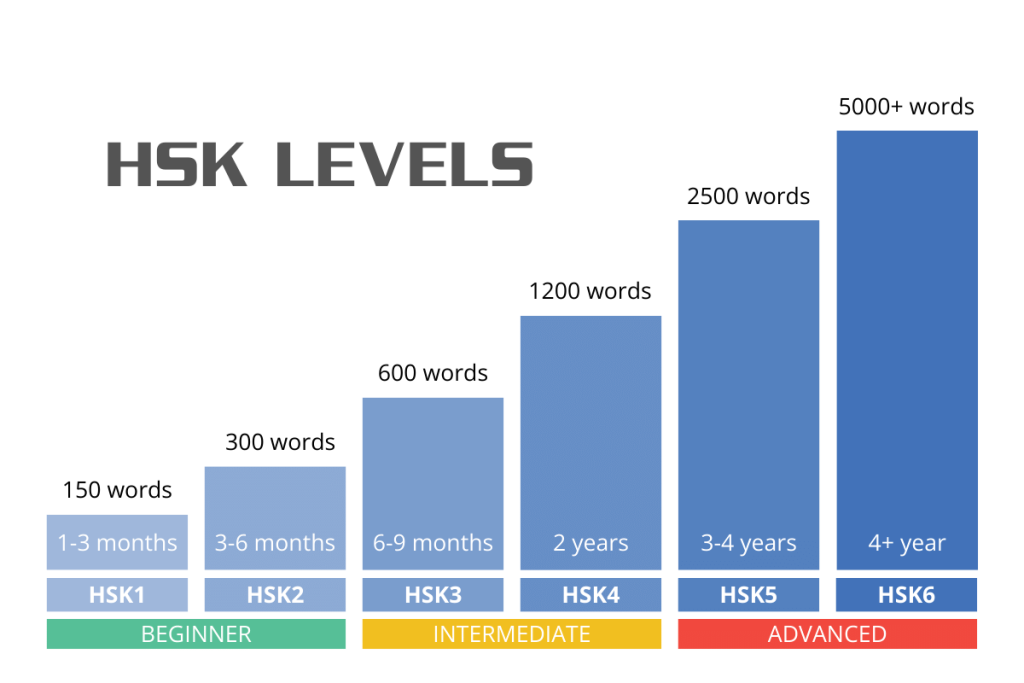
The old HSK exam has 6 levels, with Level 1 being the most basic and Level 6 being the most advanced. Each level has a different requirement for vocabulary, grammar, and sentene patterns.
| Level | Description |
| HSK 1 | Understand simple Chinese characters and sentences. |
| HSK 2 | Use basic Chinese in their daily lives. |
| HSK 3 | Use Chinese in their personal lives, studies and work, and communicate most tasks they experience. |
| HSK 4 | Discuss a wide range of topics in Chinese and communicate with Chinese speakers at a high standard. |
| HSK 5 | Read Chinese news and watch movies, as well as write and deliver a speech in Chinese. |
| HSK 6 | Understand any information communicated and smoothly express themselves in written or oral form. |
The current HSK is divided into 9 levels, grouped into three main categories: Beginner, Intermediate, and Advanced. Each HSK level requires learners to master a specific range of vocabulary and grammatical structures:
| Level | Syllables | Characters | Words | Grammar Points | |||||
| New | Cumulative | New | Cumulative | New | Cumulative | New | Cumulative | ||
| Beginner | 1 | 269 | 269 | 300 | 300 | 500 | 500 | 48 | 48 |
| 2 | 199 | 468 | 300 | 600 | 772 | 1272 | 81 | 129 | |
| 3 | 140 | 608 | 300 | 900 | 973 | 2245 | 81 | 210 | |
| Intermediate | 4 | 116 | 724 | 300 | 1200 | 1000 | 3245 | 76 | 286 |
| 5 | 98 | 822 | 300 | 1500 | 1071 | 4316 | 71 | 357 | |
| 6 | 86 | 908 | 300 | 1800 | 1140 | 5456 | 67 | 424 | |
| Advanced | 7-9 | 202 | 1110 | 1200 | 3000 | 5636 | 11092 | 148 | 572 |
Beginner Stage (Levels 1–3)
This stage equips learners with basic vocabulary, grammar, and communication skills for everyday situations.
HSK 1:
- Recognize and use around 300 common Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 500 words.
- Engage in simple conversations on familiar topics.
- Introduce yourself and others.
- Respond to basic greetings.
HSK 2:
- Recognize and use around 600 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 1,272 words.
- Communicate on basic topics related to personal and family life, shopping, locations, and work.
- Use more vocabulary and grammar structures compared to Level 1.
HSK 3:
- Recognize and use around 900 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 2,245 words.
- Participate in conversations on familiar topics.
- Describe personal experiences and events.
- Express personal opinions.
- Read simple materials such as menus, signs, and basic instructions.

Intermediate Stage (Levels 4–6)
This stage is for intermediate learners, assessing more advanced language skills, including reading comprehension, writing, and handling complex conversations.
HSK 4:
- Recognize and use around 1,200 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 3,245 words.
- Comprehend and produce written and spoken materials on various topics, such as work, studies, and daily life.
- Engage in discussions and handle more complex language tasks.
HSK 5:
- Recognize and use around 1,500 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 4,316 words.
- Understand and express opinions fluently on various topics, including social and cultural issues.
- Comprehend longer texts like articles, news, and literary works.
- Participate in in-depth conversations.
HSK 6:
- Recognize and use around 1,800 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 5,456 words.
- Comprehend and produce complex written and spoken materials.
- Handle professional and academic tasks.
- Communicate effectively in diverse contexts.

Advanced Stage (Levels 7–9)
HSK 7–9 is designed for advanced learners aiming to master high-level skills such as understanding and producing content on complex topics and communicating effectively in professional and academic settings.
- Recognize and use around 3,000 Chinese characters.
- Understand approximately 11,092 words.
- Comprehend and articulate abstract ideas.
- Use Chinese at a near-native level.
- Communicate fluently in all situations, including academic environments.
HSK Exam Structure for Each Level
By now, you should clearly understand what the HSK certificate is and the requirements for each HSK level. Next, let’s take a look at the exam structure for each HSK level:
HSK 1 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 1 exam consists of a total of 40 questions, divided into 2 parts, with 40 minutes allocated to complete the test (including time for filling in personal information and answers):
- Listening: 20 questions (15 minutes)
- Reading: 20 questions (17 minutes)
HSK 2 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 2 exam consists of 60 questions, with 50 minutes to complete the test:
- Listening: 35 questions (25 minutes)
- Reading: 25 questions (20 minutes)
HSK 3 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 3 exam consists of a total of 80 questions and 85 minutes are given to complete the test, which is divided into 3 parts:
- Listening: 40 questions (35 minutes)
- Reading: 30 questions (25 minutes)
- Writing: 10 questions (15 minutes)
HSK 4 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 4 exam consists of a total of 100 questions, and the total exam time is 100 minutes, with 3 parts:
- Listening: 45 questions (30 minutes)
- Reading: 40 questions (40 minutes)
- Writing: 15 questions (25 minutes)
HSK 5 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 5 exam consists of 100 questions, divided into 3 parts, with 120 minutes to complete the test:
- Listening: 45 questions (30 minutes)
- Reading: 45 questions (45 minutes)
- Writing: 10 questions (40 minutes)

HSK 6 Exam Structure
The HSK Level 6 exam consists of a total of 101 questions, and the total exam time is 135 minutes. The exam has 3 parts:
- Listening: 50 questions (35 minutes)
- Reading: 50 questions (50 minutes)
- Writing: 1 question (45 minutes)
HSK 7, 8, 9 Exam Structure
The exam structure for HSK Levels 7, 8, and 9 is the same, consisting of 98 questions, covering all skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and translation. The exam time for HSK Levels 7–9 is the longest, with the following sections:
- Listening: 40 questions (30 minutes)
- Reading: 47 questions (60 minutes)
- Writing: 2 questions (55 minutes)
- Speaking: 5 questions (24 minutes)
- Translation: 2 written translation and 2 oral translation questions (41 minutes)
Thus, the HSK 7–9 exams assess the candidate’s language abilities across multiple skills and require a high level of proficiency, including translation skills and professional communication.
How complicated is the HSK exam, and when will I be able to have a conversation?
In terms of difficulty and format, the HSK exams vary in complexity. The HSK 1 exam requires an average of 50 hours of practice. Whereas the HSK 4 requires an average of 60 hours. Similar to the Cambridge assessments, the HSK exams consist of listening, reading, and writing sections.
Now you may be asking at which level you can communicate in everyday situations. Depending on a person’s progress and learning style, it is better to aim for at least Level 3 to have basic communication abilities and Level 5 for more advanced conversations.
Conclusion
The HSK test not only assesses your language proficiency but also your test-taking skills, which are best developed through practice and guidance. If you’re wondering “what is HSK test?” and how to evaluate your ability to use Chinese in real-life situations, here at Ni Hao Ma, our experienced native Chinese teachers prepare students of all ages for the HSK exams.
Using interactive teaching methods and cutting-edge technology, our HSK program combines Chinese culture and language, providing an engaging and stimulating journey toward mastering the Chinese language. If you want to learn more about mastering Chinese and enjoying its many benefits, consider enrolling in our HSK courses.



