Among the most popular languages in Asia, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean are top choices for many learners. However, each language has distinct characteristics regarding script, pronunciation, grammar, and difficulty level. So, which language is the easiest to learn: Chinese, Japanese or Korea? Let’s explore this topic with Ni Hao Ma in the following article.
The Popularity of Chinese, Korean, and Japanese
The popularity of a language is a crucial factor when deciding to learn it, as it directly impacts job opportunities, communication, and daily life. A widely spoken language not only opens up career prospects but also enhances its practicality in international environments.
Chinese
With a population of 1.4 billion, China is the most populous country in the world, making Chinese one of the most widely spoken languages. It is not only prevalent in China but is also commonly used in countries such as Singapore, Taiwan, Malaysia, and communities with a significant Chinese presence.

Japanese
Japanese is a highly influential language in Asia due to Japan’s economic and technological standing. The country is home to major corporations such as Toyota, Honda, and Sony, attracting millions of foreign workers each year. Learning Japanese offers career opportunities in fields such as IT, manufacturing, and engineering.
Korean
The Hallyu wave, driven by K-pop, Korean dramas, fashion, and beauty trends, has created a global sensation, especially in Vietnam. The popularity of Korean culture has led to a surge in demand for learning the language, not only for education and work but also to gain deeper cultural insights.

Besides its cultural influence, South Korea is one of Asia’s leading economies, with major corporations like Samsung, Hyundai, LG, and SK. However, the use of Korean is mainly confined to South Korea and a few smaller communities worldwide, making it less globally applicable compared to Chinese or English.
Comparison of Difficulty: Chinese, Korean, and Japanese
Each language has unique characteristics in writing systems, grammar, pronunciation, and usage, resulting in different levels of difficulty. Below are the challenges associated with learning each language:
Chinese
- Writing System: Uses Chinese characters (汉字 – Hanzi), which are logograms rather than an alphabet. Learners must memorize thousands of individual characters to read and write fluently. Some characters have numerous strokes, making memorization and writing challenging.
- Grammar: Features a simple sentence structure, similar to Vietnamese (Subject – Verb – Object). Chinese verbs do not change based on tense, and there are no noun genders or plural forms. However, specific use of time indicators and particles requires practice.
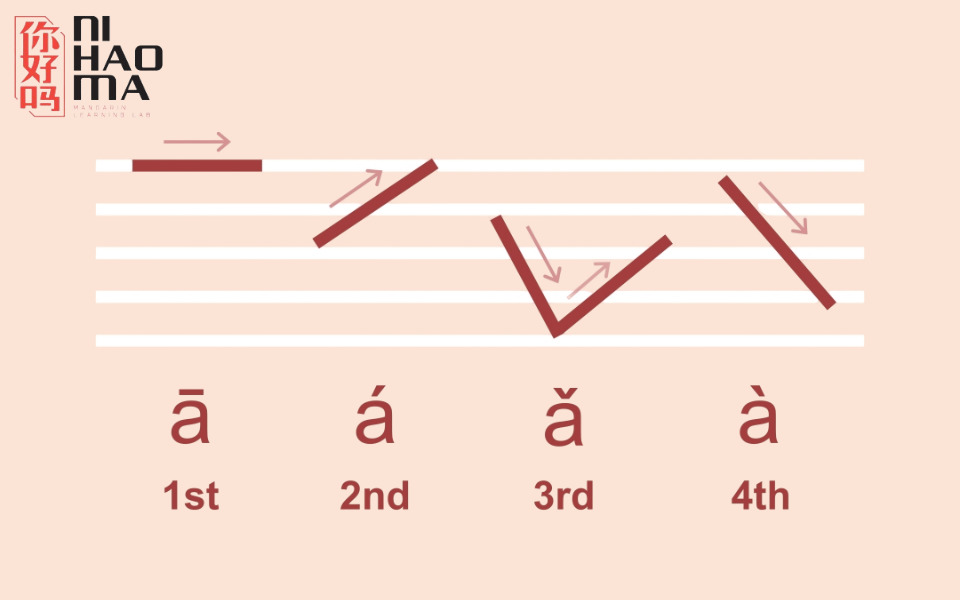
- Pronunciation: Includes four main tones, making pronunciation difficult for beginners. Incorrect tonal pronunciation can completely change the meaning of words.
Korean
- Writing System: Uses the Hangul alphabet (한글), consisting of 24 basic letters with a straightforward combination system. Hangul is considered one of the most scientific and easiest writing systems, allowing beginners to learn reading and writing within a few days.
- Grammar: More complex than Chinese, with a Subject – Object – Verb (SOV) sentence structure, differing from Vietnamese. Korean verbs conjugate based on tense, honorifics, and politeness levels, requiring learners to master various transformation rules.
- Pronunciation: Easier than Chinese and Japanese. Although some aspirated and tense sounds may be challenging initially, Korean lacks tonal variations, making pronunciation relatively straightforward.
Japanese
- Writing System: The most complex, incorporating three scripts: Hiragana (phonetic), Katakana (used for foreign words), and Kanji (Chinese characters). Kanji, borrowed from Chinese, is difficult due to its vast number of characters. Mastering Japanese requires learning all three scripts, making reading and writing much more challenging than Korean or Chinese.
- Grammar: Highly intricate, also using an SOV structure like Korean, but with additional complexities such as multiple honorifics and sentence variations based on context. The Japanese honorific system is particularly difficult due to its multiple levels of politeness, requiring careful usage.
- Pronunciation: Relatively simple, with only five vowel sounds and no tones. However, pitch accent can change word meanings, and certain sounds, like “r” and “l,” may be difficult for Vietnamese learners to differentiate.
Should You Learn Chinese, Japanese, or Korean?
Many people wonder which of these languages is the easiest to learn. However, your decision should be based on various factors, including learning objectives, personal interests, and career opportunities. Below are key considerations before making your choice:
Learning Purpose
Expanding career opportunities is one of the main reasons for learning a foreign language. If you are interested in international trade, business, or import-export, Chinese is a strategic choice. Fluency in Chinese provides advantages when working with Chinese enterprises or multinational companies with Chinese partners.

For those interested in technology, engineering, mechanics, or manufacturing, Japanese may be the better option. Japan hosts numerous global corporations like Toyota, Sony, Honda, Nissan, and Mitsubishi, which frequently recruit employees proficient in Japanese. Additionally, Japan offers various scholarships and long-term work opportunities for Vietnamese professionals.
Although Korean is not as widespread as Chinese or Japanese, it presents career opportunities in entertainment, media, fashion, beauty, and commerce. South Korean companies like Samsung, LG, and Hyundai actively hire Korean-speaking professionals in Vietnam.
Language Difficulty
Each language varies in difficulty, affecting the time and effort required to achieve proficiency. Korean is the easiest among the three due to its simple Hangul script and relatively straightforward grammar. However, verb conjugations and honorifics may pose some challenges.

Chinese is harder than Korean due to its complex character system. However, its grammar is relatively simple, and many vocabulary words resemble Vietnamese, making it easier to learn.
Japanese is the hardest, featuring an intricate writing system (Hiragana, Katakana, Kanji) and complex grammar with multiple politeness levels. It requires significant time and effort to master.
Cost of Learning
The decision to learn Chinese, Korean, or Japanese is also influenced by financial considerations. Below is a comparison of learning costs:
- Chinese: The most affordable option. A 2-3 month course costs around 2,500,000 – 3,000,000 VND. Studying in China costs approximately 4,000 USD per year, excluding living expenses.
- Japanese: Courses typically cost around 3,000,000 VND per session. Studying in Japan is expensive, averaging 15,000 USD per year, including living expenses.
- Korean: Learning Korean costs about 2,500,000 – 3,500,000 VND per course, with advanced levels reaching 5,000,000 VND. Studying in Korea costs about 3,000 USD per semester, excluding living expenses.
Conclusion
If you are wondering which language is the easiest to learn – Chinese, Japanese or Korean – this article has outlined the challenges of each language. Your choice should not solely depend on difficulty but also align with your goals and interests.
Based on your purpose for learning a foreign language and personal preferences, choose the language that best suits you and commit to mastering it. Hopefully, this article from Ni Hao Ma has provided valuable insights into the characteristics of each language, helping you make an informed decision.



